Protecting your systems and data from attack can often introduce untenable inefficiency into your corporate IT operations. You find yourself wading through treacle just trying to stay safe.
A great way to relieve this unwanted torpor is to implement an effective Identity and Access Management System (IAM). By now, all enterprises should have them, but many don’t, especially SMBs. Awareness is growing, though, and so is the Identity Management space.
What is IAM?
IAM involves granting (or indeed, restricting) access to an organisation’s digital assets to allowed users, depending on context. These may be employees, customers, business allies or other trusted parties. A good IAM system allows administrators to do this efficiently with high levels of automisation and increased sophistication (e.g. machine learning).
The tools under the umbrella of IAM will include password-management, provisioning software, security-policy enforcement applications, reporting and monitoring, and identity repositories.
An effective IAM system should include most of the following:
Access management: processes and technologies used to control and monitor network access. Includes: authentication, authorisation, trust and security auditing, both on-premises and cloud-based systems. Biometric authentication: Including fingerprint sensors, iris and retina scanning, and facial recognition. Not for everyone yet, but a growing area. Context-aware network access control is a policy-based method of granting access to network resources according to the current context of the particular users. Credential is a user identifier to access to a network: the user’s password, public key infrastructure (PKI) certificate, or biometric information. De-provisioning: removing an identity from an ID repository and terminating access privileges. Digital identity: a central feature, the ID itself, including user and that person’s or entity’s access privileges. Entitlement: attributes that specify the access rights and privileges of an authenticated security principal. Identity as a Service (IDaaS): Cloud-based IDaaS offers identity and access management functionality to an organisation’s systems that reside on-site and/or in the cloud. Identity lifecycle management: the entire set of processes and technologies for keeping digital identities current. This will include identity synchronisation, provisioning, de-provisioning, and the ongoing management of user attributes, credentials and entitlements. Identity synchronisation: ensuring that multiple identity stores—e.g. mergers and acquisitions—contain consistent data for a given digital ID. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP): an open standards-based protocol for managing and accessing a distributed directory service, such as Microsoft’s AD Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is when more than just a single factor, such as a user name and password, is required for authentication to a network or system. At least one additional step is also required, such as email or SMS authentication. Password reset is a feature of the ID management system that allows users to re-establish their own passwords. The application asks for a secret word or a set of questions to verify the user’s identity. Privileged account management: managing and auditing accounts and data access based on the privileges of the user. A privileged user has been granted administrative access to systems. He or she, for example, would be able set up and delete user accounts and roles. Provisioning is the process of creating identities, defining their access privileges and adding them to an ID repository. Risk-based authentication (RBA) dynamically adjusts authentication requirements if the user is attempting authentication in an unusual way or from an unusual location. Single sign-on (SSO): Access control for multiple separate systems. With one username and password, a user can access a system or systems without using different credentials. User behavior analytics (UBA): examines behaviour and applies algorithms and analysis to detect anomalies that may reveal potential threats.
________________________________________________________________________
Where to start? There are many vendors offering IAM solutions, but we’d recommend you take a look at ManageEngine’s AD360.
With over six years of success behind it, AD360 is technically mature – a sophisticated, powerful and cost-effective IAM solution. Security managers and admins employ it to manage user identities, control access to resources, enforce security, and – an ever-growing challenge – to ensure compliance.
AD360 provides user provisioning, self-service password management, and Active Directory change monitoring, to single sign-on (SSO) for enterprise applications. What’s more, it helps you perform all your IAM tasks with a simple, easy-to-use interface.
AD360 delivers all this functionality for Windows Active Directory, Exchange Servers, and Office 365. You can just choose the modules you need and start addressing IAM challenges across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments from within a single console.
__________________________________________________________________________
ManageEngine technology is used by tens of thousands of companies worldwide including 60% of Fortune 500 enterprises.
Contact us to get more information about AD360, receive a formal quotation or for any pre-sales advice and support:
[email protected] |
020 8733 7103
Wichtige Eckdaten:
- Verfügbarkeit: Nutzer von E-Commerce und der Testversion haben sofortigen Zugriff. Nutzer ohne E-Commerce-Zugang müssen ihren Administrator darum bitten, die Funktionen der generativen KI über die Admin-App zu aktivieren.
- Genauigkeit: Da es sich um eine Beta-Funktion handelt, können die Antworten vereinzelt Ungenauigkeiten oder Inkonsistenzen aufweisen. Durch kontinuierliche Updates wird jedoch eine stetige Verbesserung der Zuverlässigkeit angestrebt.
- Datenschutz und Sicherheit: Dokumenteninhalte werden während der Verarbeitung temporär gespeichert und nach Abschluss der Aufgabe umgehend gelöscht. Nutzerdaten werden nicht zur Schulung von KI-Modellen verwendet.
- Beta-Status: Der Dokumentenassistent befindet sich derzeit in der Beta-Phase. Obwohl die Funktion vollständig einsatzfähig ist, wird sie fortlaufend weiterentwickelt. Das Feedback der Nutzer spielt eine entscheidende Rolle für die weitere Optimierung.
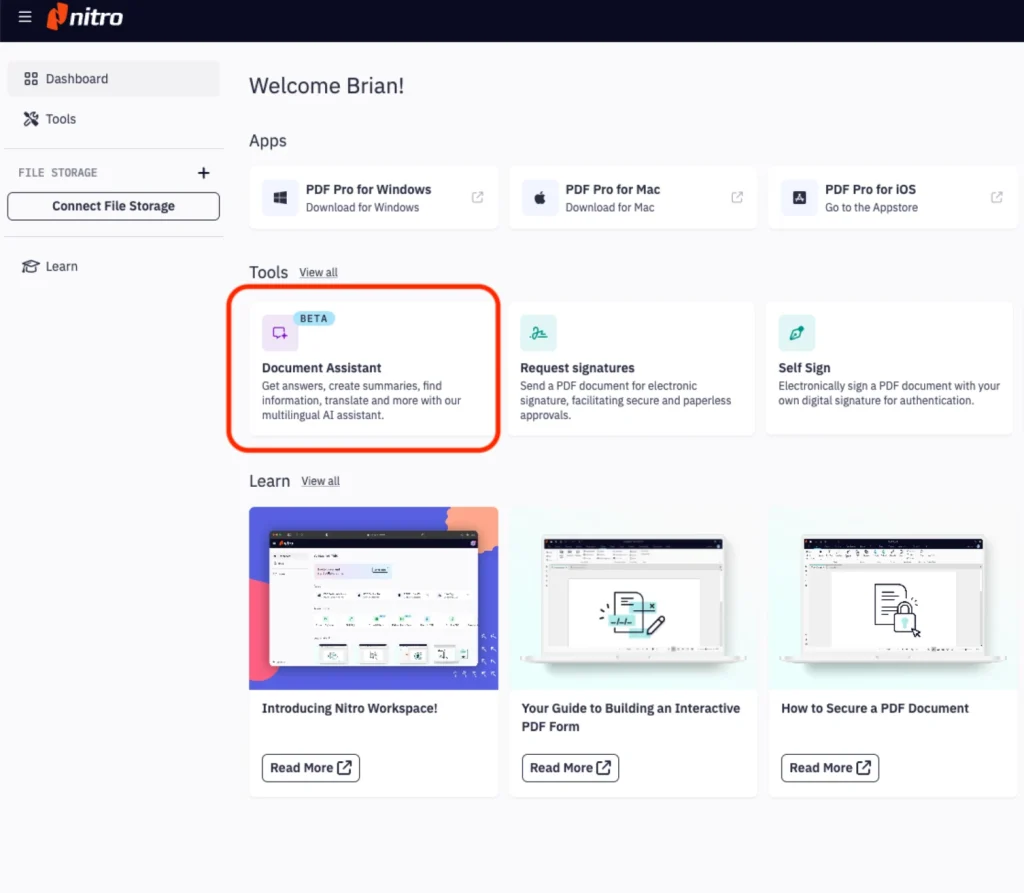
Zugang zum Nitro Dokumentenassistenten
Der Einstieg in den Nitro Dokumentenassistenten ist unkompliziert. Das Tool unterstützt PDF-Dateien mit einer maximalen Größe von 25 MB. Folgen Sie diesen Schritten:
- Öffnen Sie Nitro Workspace und navigieren Sie zum Bereich „Tools“.
- Klicken Sie auf das Symbol „Dokumentenassistent“.
- Laden Sie das Dokument hoch, indem Sie eine Datei auswählen oder die Drag-and-Drop-Funktion nutzen.
So meistern Sie den Nitro Dokumentenassistenten
Nach dem Hochladen eines Dokuments erstellt der Nitro Dokumentenassistent eine Zusammenfassung und schlägt erste Fragen für die Interaktion vor.
Für maßgeschneiderte Anfragen wird den Nutzern empfohlen, ihre Eingaben klar, präzise und spezifisch zu formulieren. Hier einige Beispiele für mögliche Anfragen:
- Fasse dieses Dokument für mich zusammen.
- Fasse es stichpunktartig zusammen.
- Fasse dieses Dokument für mich auf Spanisch zusammen.
- Liste die externen Quellen auf, die in diesem Dokument genannt werden.
- Finde Inhalte zu den Zahlungsbedingungen in diesem Vertrag.
- Erkläre mir die wichtigsten Punkte [dieses Vertrags] in einfacher Sprache.
- Schreibe dieses [Benutzerhandbuch] als FAQ um.
- [In diesem französischen Mietwagenvertrag] Kann ich eine Debitkarte verwenden, um ein Auto zu mieten? Antworte bitte auf Englisch.
Wichtige Hinweise zu Sicherheit und Datenschutz für Ihre Kunden
Nitro legt großen Wert auf Sicherheit und Datenschutz. Dokumente werden während der Verarbeitung nur vorübergehend gespeichert und nach Abschluss des Vorgangs sofort gelöscht. Zudem stellt Nitro sicher, dass Kundendokumente niemals zur Schulung von KI-Modellen verwendet werden. Diese Maßnahmen schützen sensible Informationen und geben Ihren Kunden ein beruhigendes Gefühl.
So verbessern Sie den Nitro Dokumentenassistenten
Nitro schätzt das Feedback der Nutzer zur kontinuierlichen Verbesserung des Dokumentenassistenten. Nach jeder Interaktion werden die Nutzer gefragt: „War dies hilfreich?“ Sie können mit „Daumen hoch“ oder „Daumen runter“ antworten.
Für detaillierteres Feedback können die Nutzer die Feedback-Seite des Nitro Knowledge Assistant besuchen, um zur Weiterentwicklung des Tools beizutragen.
Ermöglichen Sie Ihren Kunden Erfolg mit Nitro, unterstützt durch KI
Der Nitro Dokumentenassistent ist ein wertvolles Tool, um Ihren Kunden zu helfen, ihre Dokumentenabläufe zu optimieren. Ob sie Nitro zum ersten Mal ausprobieren oder von einem anderen PDF-Anbieter wechseln, diese KI-gestützte Funktion zeigt Nitro’s Engagement für Innovation.
Wenn Sie Fragen zu Nitro-Lizenzen oder erfolgreichen Verkaufsstrategien für Nitro-Lösungen haben, wenden Sie sich an das Team von QBS. Wir unterstützen Sie gerne auf Ihrem Weg zum Erfolg mit Nitro!
 Protecting your systems and data from attack can often introduce untenable inefficiency into your corporate IT operations. You find yourself wading through treacle just trying to stay safe.
Protecting your systems and data from attack can often introduce untenable inefficiency into your corporate IT operations. You find yourself wading through treacle just trying to stay safe. Protecting your systems and data from attack can often introduce untenable inefficiency into your corporate IT operations. You find yourself wading through treacle just trying to stay safe.
Protecting your systems and data from attack can often introduce untenable inefficiency into your corporate IT operations. You find yourself wading through treacle just trying to stay safe.